Learn about Crypto and Decentralized Finance

The Crypto 101 series describes the basic concepts required for any one new to crypto to gain a decent understanding of what cryptocurrency is and how it works. We’ve written a few useful guides already within the Crypto 101 series including the risks of investing in cryptocurrencies, how and where to buy crypto, how to withdraw from exchanges, and how to smartly invest in cryptocurrencies.
In this article you will learn about the leading trend in crypto of 2020/2021 — DeFi or Decentralized Finance. In Part 1 we will introduce the related terms, examples and sources.
Decentralized Finance emerged in 2018, but became widely spread in 2020 when such protocols as Yearn.Finance, Curve and other have taken the financial world by storm.
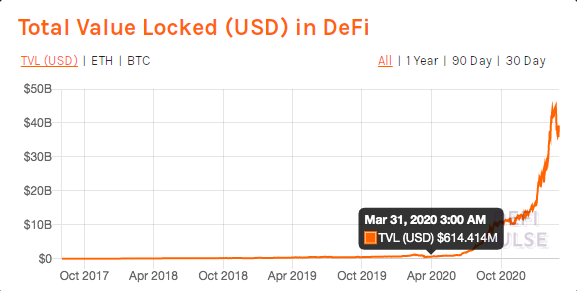
DeFi is simply defined as a form of finance that doesn’t rely on any central financial intermediary but instead uses a set of smart contracts for its operations and a governance token with which all decisions are made.
DeFi gives an opportunity for everyone to earn and take part in the wonder that is cryptocurrency, regardless of whether or not they have deep pockets. DeFi is for everyone!
Throughout this article, you will see the term “Smart Contract” mentioned a lot. A smart contract is defined as a set of instructions that are capable of executing themselves without the need for human input. For instance, a smart contract that is coded to send $5 to your friend on their birthday will do exactly that without any input from you as long as the account you’re sending from is funded.
Equally, you may see the term “liquidity pool” a lot as well. A liquidity pool is a collection of tokens that facilitates swaps on decentralized exchanges. These tokens are always added in a 50:50 ratio. For example, if you wanted to add liquidity to the ETH/USDT pool, you would have to add 50% ETH and 50% USDT. Liquidity providers (LPs) are given LP tokens representing their liquidity and stake in the liquidity pool.
Decentralized Exchanges
Let’s start from Decentralized exchanges (or DEXs), like Uniswap, Balancer or SecretSwap. These services allow users to swap one token to another through a set of smart contracts powering special liquidity pools.
These liquidity pools require users to add liquidity to them, which makes it decentralized as the liquidity belongs to the users. As a reward for adding liquidity, users are rewarded with a percentage of the swap fees the exchange obtains.
Decentralized exchanges allow users to have full custody over their cryptocurrency, making it less susceptible to hacks and exploits. There is also no issue of frozen funds, an issue that plagues centralized exchanges to date.
A good example of a DEX and liquidity provision platform is SecretSwap.
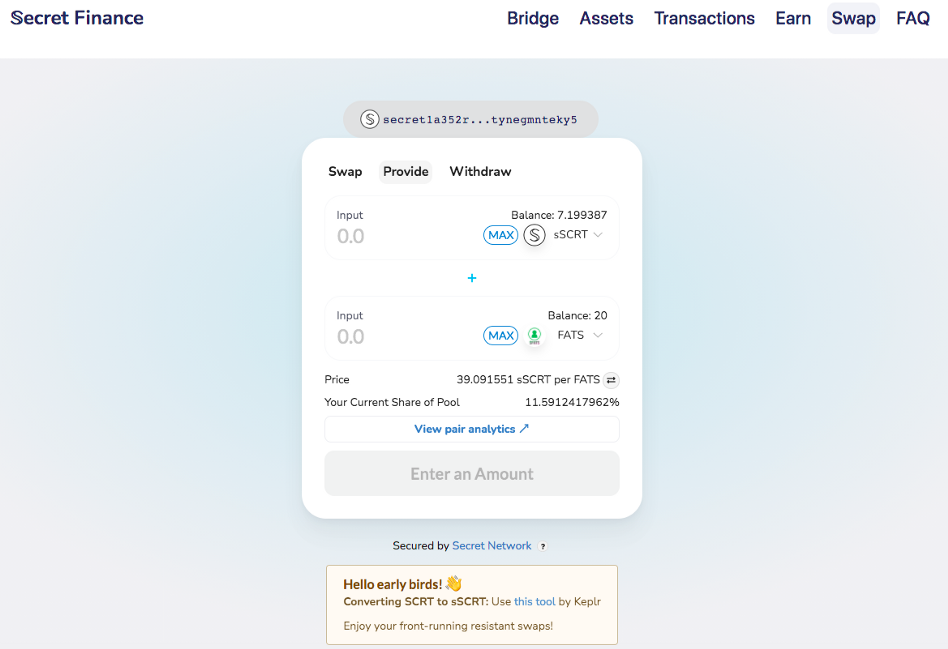
SecretSwap is a DeFi exchange platform that offers low fees and is privacy preserving. In other words, your private information stays secret when trading on SecretSwap. Secret Network also offers a feature that prevents front-running, and support wrapped versions of all major ERC-20 tokens.
Secret Network is constantly innovating, and is rolling out a Binance Chain bridge soon. Check out the article here!
Learn more about DEXs and how they work here.
Lending and Borrowing
Next up, we have Lending and Borrowing protocols like Compound and Aave. These protocols allow for decentralized borrowing and lending of cryptocurrencies without the need for a central body like a bank to issue the loans.
Once again, liquidity pools are utilized to offer the loans to prospective borrowers, and users that add tokens to these pools are rewarded with a portion of the fees paid to the platform by users.
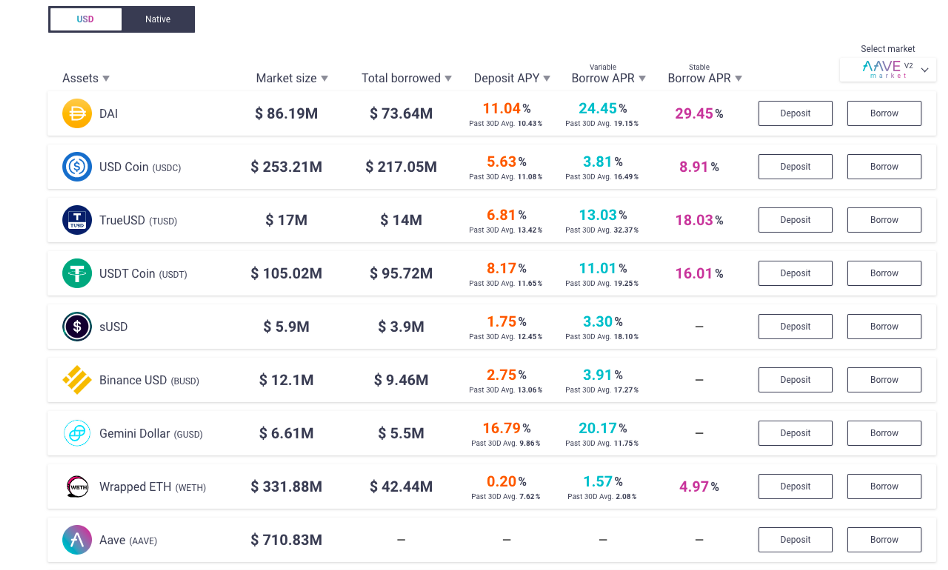
The Aave Landing Platform
Aave is a popular lending and borrowing protocol that allows anyone to take out loans or provide liquidity for loans. Taking out loans involves depositing collateral for the loan, which ensures that the liquidity never dries up.
Liquidity providers are given Aave interest bearing tokens when they provide liquidity for loans. This allows them to track their interest in real time and always be covered in the case of an exploit in the smart contracts.
Decentralized lending and borrowing was a major breakthrough in the DeFi sector.
Staking Platforms
Equally, there are yield farms and staking platforms which allow users to delegate one cryptocurrency token to earn more of the delegated token or another token entirely.
Staking is the process of contributing to the network of the token by actively participating in network transaction validation. Staking usually gives rewards in the token you stake. It’s the most secure and easy way to earn passive income in the DeFi world.
Citadel.one is a great place to stake your cryptocurrencies and watch your earnings pour in real time! Learn more about staking with Citadel.one here.
Yield farming on the other hand is the staking of one token to earn another token entirely. This method is popular on many platforms which want to launch another token fairly.
Derivatives
Derivatives are tradable securities or contracts that derive their value from an underlying asset. They include investment products such as contracts for difference, options and futures.
Most famous example of such project is Synthetix.io. Synthetix is an Ethereum-based protocol for the issuance of synthetic assets. Analogous to derivatives in legacy finance, synthetic assets are financial instruments in the form of ERC-20 smart contracts known as “Synths” that track and provide the returns of another asset without requiring you to hold that asset.
DeFi Insurance
Yes, there are also decentralized alternatives to traditional insurance. The leading company in this sphere is Nexus Mutual. It replaces the idea of a traditional insurance company, because it is wholly owned by the members. The model encourages engagement as members will get economic incentives for participating in Risk Assessment, Claims Assessment and Governance.

Nexus Mutual
DeFi is a powerhouse, and now you know the basics of it! In Part 2 we will talk more about how DeFi works, how it’s structured, introduce more projects and ways to earn with DeFi. Stay tuned!
You can get started using DeFi and DeFi products on Citadel.one right now.
Also we welcome to subscribe to our blog on Medium, and check our latest DeFi Recap here.
Useful links
The risks of investing in cryptocurrencies
How and where to buy crypto
How to withdraw from exchanges
How to smartly invest in cryptocurrencies
About Citadel.one
Citadel.one is a non-custodial Proof-of-Stake platform for the management and storage of crypto assets. Users can create public addresses for all supported networks with one seed phrase, connect their Ledger or Trezor device, or import an address generated by another wallet.
The analytical dashboard provides relevant information on wallets’ balances and networks’ main metrics. In Citadel.one, we standardize the semantics, making interactions with the platform as easy as possible. The same goes for network metrics. By using universal terms, we are making it easier for users to understand and compare networks.
One of the main functions of the Citadel.one platform is participation in the PoS consensus — users can stake and delegate their assets, claim rewards, and follow the latest network proposals in the voting tab.
Citadel.one offers its users instant cryptocurrency exchange services that allow fast and secure crypto assets swap. It is also possible to buy and sell crypto with a credit or debit card. Citadel.one users can track rewards, withdrawals, transfers, and deposits across all supported networks and add comments to these transactions.
Among PoS platforms, Citadel.one supports Secret Network ($SCRT), Cosmos ($ATOM), ICON ($ICX), IOST, Orbs, and Tezos ($XTZ). We also support Ethereum, Bitcoin, and Tether ($USDT) for our users’ convenience. Mobile and desktop versions, new networks, including Polkadot and Ontology, are scheduled for the upcoming updates. Furthermore, delving into the idea of true decentralization, we envision Citadel.one a decentralized autonomous organization and a genuinely community-owned platform in the nearest future.